Debund | "Tao" Listen to "Way" Talk about the Time Limitation and Period of the General Provisions of the Civil Code(Part 2)
三、 Application of limitation of action
In principle, the limitation of action applies to the right of claim. For the right to form and change legal relations, it mainly applies to the exclusion period. For all kinds of arbitration cases, if there are no special provisions, the provisions on limitation of action can be applied in principle. In the dispute settlement of arbitration and litigation, the court, arbitration commission and other judicial institutions should not actively apply the limitation of action and arbitration, but the obligor should exercise the right of defense, and the obligor can agree to continue to perform its obligations without exercising the right of defense.
(一) Right of Claim and Limitation of Action
According to the different ways of realizing civil rights and their functions, civil rights can be classified into the right of domination, the right of claim, the right of defense and the right of formation. According to the general theory, the limitation of action is limited to the exercise of the right of claim, and the limitation of action is not applicable to the right of revocation, the right of rescission and other rights of formation and the right of defense.
1. Claim right applicable to limitation of action
(1) Reasons for the Application of Prescription of Claim
The truth is that the realization of all claims depends on the obligee's request for the other party to do or not to do something. Therefore, during this period, the relative parties of all claims are in a state of indecision. The elimination of such a state is exactly where the function of the extinctive prescription system lies. It is impossible to exercise the right of domination, the right of defense and the right of formation, but it is also applicable to the right of claim for damages in the relief right transformed from the infringement of the right of domination.
(2) Specific applicable claim types
The claim with the nature of creditor's right is the most typical applicable object of limitation of action; In addition to the special provisions analyzed later, the claim of real right is also regulated by the limitation of action, and it is the same as the claim of creditor's right in terms of the length of the period and the starting point; In principle, the right of intellectual property claim also applies to the limitation of action; The system of limitation of action is also applicable to the claim for compensation when the personality right is infringed and the claim for compensation based on the status relationship.
2. Claim not applicable to limitation of action
(1) Non application of Article 196 of the Civil Code
The limitation of action shall not apply to the request for ceasing the infringement, removing the obstruction and eliminating the danger. As a part of the function of real right, the right of real right claim to stop infringement, remove obstruction and eliminate danger shall not be extinguished upon expiration of prescription. Similarly, the limitation of action does not apply to claims of absolute rights, such as personal rights and intellectual property rights, which involve the cessation of infringement, the removal of obstacles and the elimination of risks.
The obligee of the real right of immovable property and the registered real right of movable property requests the return of property, and the limitation of action shall not apply. Whether it is real property or movable property, registration has publicity and credibility, and trust interest is an important interest in civil law. The protection of reliance interest by law is of great significance to the maintenance of the effectiveness of the new civil legal relationship and the stability of the whole social and economic order.
The limitation of action shall not apply to claims for the payment of alimony, alimony or maintenance. Although the payment of alimony, alimony and alimony has the content of property delivery, it is first reflected in the right to claim for identity interests, especially the protection of the interests of vulnerable groups, and the basic right to survival of the people concerned. If the obligor fails to pay the above expenses after the expiration of the time limit, the life of the obligee will not be guaranteed, which is not only against the principle of public order and good customs, but also against humanistic care.
For other claims for which the limitation of action is not applicable according to law, this provision is an all inclusive clause. The preceding content does not completely list the claims that are not applicable to the limitation of action system, so it can be used as a basis to meet the requirements of the complexity and diversity of trial practice, and also pave the way for the connection with judicial interpretation.
(2) Circumstances where the provisions of judicial interpretation are not applicable
The newly issued Judicial Interpretation of the General Provisions has nothing to do with this issue, but the first article of the Prescription of Action amended in 2020 lists the specific circumstances: the right to claim the payment of the principal and interest of deposits; The right to claim the principal and interest of treasury bonds, financial bonds and corporate bonds issued to unspecified objects; The right to make capital contribution based on the investment relationship. These exceptions are basically based on policy judgments such as survival interests, social public interests or transaction security.
(二) Right of Formation (Exclusion Period) and Limitation of Action
1. Exclusion period applicable to formation right
The right of formation refers to the right that can take effect according to the unilateral intention of the obligee to change the corresponding legal relationship, such as the right of ratification, the right of revocation and the right of rescission. Similar to the right of control, both of them rely on the will of the obligee to achieve the effect of rights. The difference is that the right of formation does not dominate the specific object of rights, or "object" means the legal relationship to be changed. The proposition of the theory of right of formation expands the scope of rights and is known as an important discovery in law .
The exercise of the right of formation can directly change the legal status of the other party, and its effect is far stronger than the right of claim. If the obligee fails to exercise the right for a long time, the uncertainty of the legal status of the counterpart will be far greater than the claim. In view of this, the establishment of exclusion period system refers to the duration of a certain right prescribed by law or agreed by the parties. Upon expiration of the period of exclusion, the right of formation shall be extinguished. The exclusion period is the right preset period, with the goal of promoting the legal relationship to be determined as soon as possible. After the exclusion period, either the original uncertain legal relationship will be clearly fixed or the existing legal relationship will be eliminated.
2. Difference between Exclusion Period and Limitation of Action
(1) Applicable objects are different
The exclusion period is generally applicable to the formation right; Limitation of action generally applies to claims.
(2) Different effects apply
After the expiration of the exclusion period, the substantive rights are extinguished; After the limitation of action expires, the substantive rights are not extinguished, and the other party forms the right of defense.
(3) Different calculations when applicable
The exclusion period shall be calculated from the time when the right is established, and shall not apply to suspension, interruption or extension; The limitation of action shall be calculated from the date on which the obligee knew or should have known that his rights had been infringed and the obligor, and shall be a variable period, subject to the circumstances of suspension, interruption or extension.
(4) Different application in judicature
In principle, the parties can freely agree on the exclusion period, and the court can adopt the authority doctrine model to apply; In principle, the limitation of action excludes the agreement of the parties, and the court cannot actively apply the limitation of action.
(5) Legislative technology and value orientation are different
During the period of exclusion, the specific system is scattered among the subdivisions of the Civil Code, and the function of the norm is to maintain the original state of fact; There are abstract general rules and systems of limitation of action in the General Provisions of the Civil Code, while there are special systems scattered in the Subdivision and Civil and Commercial Specific Law. The normative function is to maintain the new state of fact.
3. Application of Exclusion Period
(1) The general provisions of the Civil Code have made provisions in principle, and the specific system of exclusion period is scattered in the various subdivisions of the Civil Code
Article 199 of the Civil Code stipulates that the period of exclusion stipulated by law or agreed by the parties shall be calculated from the date on which the obligee knew or should have known of the creation of the right, and the provisions on the suspension, interruption and extension of the limitation of action shall not apply, so the period of exclusion is a fixed period.
The author sorts out the exclusion period of the right of formation stipulated in the General Provisions and various sub parts (mainly embodied in the contract part, marriage and family part):
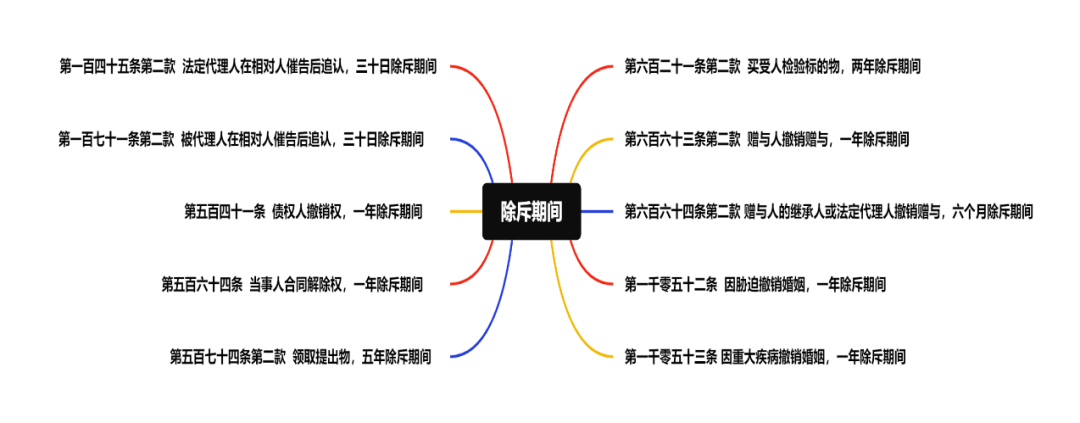
(2) Circumstances of exercising the right of formation through litigation and arbitration
In the previous lecture on "civil law practice", according to the clear provisions of the Civil Code, the author analyzed that: the legal representative's right of ratification or revocation of civil legal acts taken by persons with limited capacity for civil conduct can be exercised by reaching the other party with notice, while "the revocation right under fraud, major misunderstanding, coercion and obvious unfairness must be exercised through litigation or arbitration", The author believes that this is the way of legal fiction, which stipulates that part of the formation right is exercised through litigation or arbitration. However, according to the provisions of the Civil Code on the exercise period, the exclusion period is still applicable. The author sorts out the provisions of the general provisions and the sub parts (mainly in the property rights section, the contract section, and the marriage and family section) that "the right of formation shall or may be exercised" through litigation and arbitration, and the applicable provisions of the exclusion period. The specific statistics are as follows:
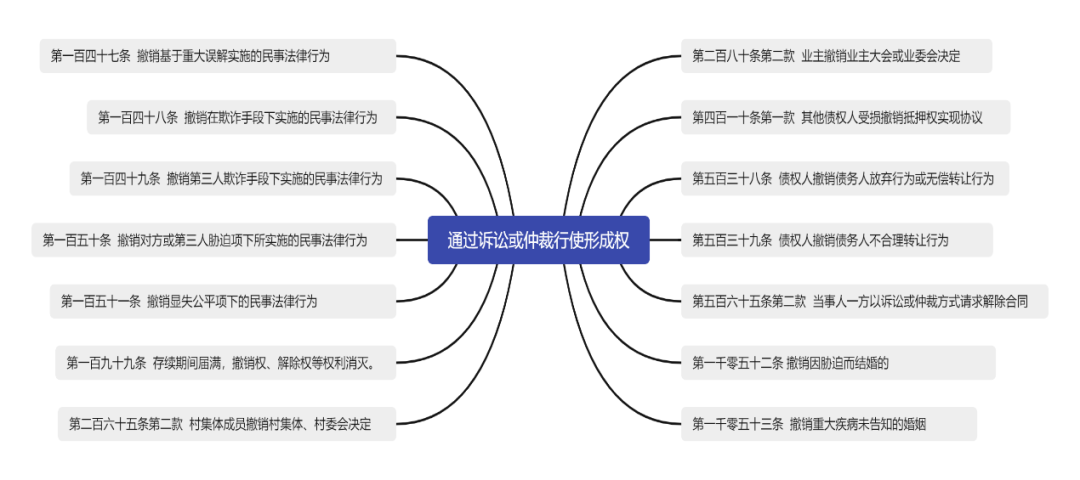
(三) Arbitration Limitation and Litigation Limitation
Litigation and arbitration are the conventional dispute settlement methods for civil and commercial disputes. Although the limitation of action and arbitration are different in the subject of jurisdiction of specific cases, they are consistent in the nature of the system and functional role. Article 198 of the Civil Code stipulates: "If the law has provisions on the limitation of arbitration, the provisions shall prevail; if there are no provisions, the provisions on the limitation of action shall apply." The author sorts out the provisions on time limitation of various arbitration as follows:
1. Civil and commercial arbitration
Civil and commercial arbitration refers to the request between natural persons, legal persons or other organizations with equal subjects to arbitration institutions for adjudication of contract disputes or other property rights disputes. Article 74 of the Arbitration Law stipulates: "If the law has provisions on the limitation of arbitration, such provisions shall apply. If the law has no provisions on the limitation of arbitration, the provisions on the limitation of action shall apply.". In combination with the provisions of the Civil Code and the Arbitration Law on the limitation of action and arbitration, the legislature, on the basis of summing up previous legislative and judicial experience, has linked the limitation of action with the limitation of arbitration. That is, in the absence of special provisions, the limitation period of arbitration is also three years, which also applies to the suspension, interruption and extension of the limitation of action.
2. Labor and personnel dispute arbitration
Labor arbitration refers to the process in which the parties ask the labor arbitration commission for arbitration in person to settle labor disputes. Article 27 of the Law on Mediation and Arbitration of Labor and Personnel Disputes stipulates: "The limitation period for applying for arbitration of labor disputes is one year. The limitation period for arbitration shall be calculated from the date when the parties know or should know that their rights have been infringed." Interruption occurs when one party claims rights from the other party, or requests rights relief from the relevant department, or the other party agrees to perform obligations. If the parties are unable to apply for arbitration during the arbitration period due to force majeure or other justified reasons, the time limit for arbitration shall be suspended.
According to Article 2 of the Provisions on the Handling of Personnel Disputes, personnel disputes between staff members and public institutions, mass organizations, civil servants under the appointment system and the organs applicable to the Civil Servant Law, and between military civilian personnel and military employing units may be submitted to the Personnel Dispute Arbitration Commission for arbitration. Article 27, paragraph 1, and Article 52 of the 2013 Reply of the Supreme People's Court on the Calculation of the Time Limitation Period for Applying for Arbitration of Personnel Disputes stipulates: "If the parties apply for arbitration within one year from the date they know or should know that their rights have been infringed, and the arbitration institution accepts the application, the people's court shall recognize it." It can be seen that the arbitration period for personnel disputes is also one year.
3. Arbitration of disputes over rural land contractual management
The arbitration of rural land contract and management disputes is that the parties apply to the rural land contract and management arbitration committee for arbitration on rural land contract and management disputes. Article 18 of the Law on Mediation and Arbitration of Rural Land Contracted Management Disputes stipulates that "the time limit for applying for arbitration of rural land contractual management disputes is two years, counting from the date on which the parties know or should know that their rights have been infringed."
(四) Application of Limitation of Action in Dispute Resolution
1. Statutory limitation of action, excluding free disposition of parties
Article 197 of the Civil Code is about the legality of the limitation of action. It is to learn from foreign legislation and absorb the content of Article 2 of the Provisions on Limitation of Action.
(1) Excluding the period, calculation method and reasons for suspension and interruption of the limitation of action agreed by the parties
The first paragraph stipulates that: "The period, calculation method and reasons for suspension and interruption of the limitation of action shall be stipulated by law, and the agreement of the parties shall be null and void." If the parties agree that the limitation of action is two years, adopt the calculation method of working days, and create reasons for suspension and interruption that are not stipulated by law, it shall be null and void.
(2) Excluding the parties from giving up the benefit of limitation of action in advance
The second paragraph stipulates: "The parties' waiver of the interests of limitation of action in advance is invalid". For example, before the expiration of the contract performance period, the limitation of action has not yet started to calculate, and the parties have not yet obtained the benefits of the limitation. If the parties give up in advance, the agreement is invalid. However, the interests of the limitation period may be disposed of freely: the obligor may exercise the right of defense; You may also waive the defense and agree to perform.
2. The court cannot actively apply the limitation of action
Article 193 of the Civil Code stipulates that "the court shall not actively apply the provisions of the limitation of action", which upgrades the content of the judicial interpretation of Article 3 of the original Provisions on the Limitation of Action to a legal provision. Article 219 of the Judicial Interpretation of the Civil Procedure Law, as a supporting measure, also stipulates that: "If a party brings a lawsuit beyond the limitation period, the people's court shall accept it. After accepting it, the other party raises a plea of limitation, and the people's court decides to reject the plaintiff's claim if it believes that the reason for the plea is justified."
The limitation of action is essentially a right of defense of the obligor, which belongs to the category of the right of free disposition, and the judiciary should not interfere too much, which is the embodiment of the principle of litigation disposition and the principle of civil law autonomy. The people's court shall not take the initiative to apply the limitation of action and the defences during the limitation of arbitration, nor shall it take the initiative to apply the suspension, interruption or extension of the limitation of action or the limitation of arbitration. Whether the people's court exercises the power of interpretation is still controversial in the judicial practice. However, for a case where a lawyer acts as an agent for a party, it is necessary to first grasp the issue of limitation of action. As a plaintiff's lawyer, it is necessary to judge whether the case filed has exceeded the limitation of action; As the defendant's lawyer, we should pay more attention to whether we can have the conditions of prescription defense.
3. It is up to the obligor to decide whether to exercise the right of defense
Article 192 of the Civil Code gives the obligor the right to decide whether to exercise the right of defense.
(1) At the expiration of the limitation period, the obligor has the right to raise a defense against non performance
As mentioned earlier, the effectiveness of the limitation of action in China has experienced a transformation from "the elimination of the right to win the case" to "the elimination of the right to defend". The so-called right of defense can be divided into broad sense and narrow sense. In a broad sense, the right of defense is the right of confrontation that prevents others from exercising their rights, and puts forward the claim of exemption or mitigation of their civil liability; The narrow sense of the right of defense refers to the right to specifically fight against the right of claim. The right of defense specifically includes the right of uneasy defense, the right of prior performance defense, the right of limitation defense, etc.
If the limitation of action specified in the first paragraph of this Article expires, the obligor has the right to defend against refusal to perform its obligations, and the obligee can no longer request to compel the obligor to perform its obligations, and the right to defend against limitation of action is a permanent right of defense in terms of the effect of its exercise. According to the provisions of Article 4 of the original Provisions on Limitation of Action, the obligor shall raise a plea of expiration of the limitation period before the end of the debate in the first instance. In principle, the prescription defense right is proposed before the end of the court debate in the first instance, which conforms to the basic legal principle of procedural stability and the principle of equal rights, and also conforms to the legislative purpose of setting the focus of disputes between the parties in the first instance procedure. It is also legitimate and reasonable from the perspective of substantive justice and litigation efficiency.
(2) After the expiration of the limitation period, the obligor's consent or voluntary performance shall be deemed as waiver of defense
The second paragraph of this article, on the basis of drawing on the experience of foreign legislation and considering China's judicial practice, integrates the contents of Article 138 of the General Principles of the Civil Law, Article 171 of the Opinions of the General Principles of the Civil Law and Article 22 of the original Provisions on Limitation of Action, stipulates that the obligor may waive the defense of the expiration of the validity of the litigation: first, agree to perform, such as issuing a repayment plan to the creditor by oral or written exercise, or both parties reach a new repayment agreement, Or voluntarily guarantee the debts after the expiration of the limitation period; The other is voluntary performance, such as actual repayment, entrusting others to perform on behalf of others, offsetting the unexpired creditor's rights with the overdue debts, etc. If the obligor voluntarily performs part of the debt, according to Article 16 of the original Provisions on Limitation of Action, if the obligor only voluntarily performs part of the debt, the remaining part shall also be deemed as agreed to perform.
In judicial practice, the documents signed or sealed by the debtor can be divided into two categories in nature: one is the documents recognizing the existence of creditor's rights, such as confirmation letters, statements, confirmations, bills of arrears, etc. If there is no intention to require performance on these documents, the signature and seal of the debtor only represents the recognition of the existence of creditor's rights that have expired during the limitation period of action, and does not lead to the waiver of litigation interests; The other is the documents that agree to perform the creditor's rights, such as payment reminder, letter of performance within a time limit, etc. If there is an intention to require performance on these documents, and there is no evidence to show that the debtor's signature or seal only indicates the receipt of the above documents, according to the provisions of the Reply of the Supreme People's Court on the Legal Effect of the Borrower's Signature or Seal on the Payment Reminder beyond the Effective Period of Litigation, the debtor shall be deemed to agree to perform, Give up the benefit of prescription.
四、 Period calculation
Period is an important legal fact, which is the basis for the occurrence, change and termination of civil legal relations, including period date and period. It is generally said that the date is the time of observation from the static side, and the period is the time of observation from the dynamic side. The date is the point, and the period is the line. Periods and periods can function independently or in combination with other facts in the form of establishing special legal facts.
As far as the independent effect is concerned, the date and period only have the meaning of time mark or measurement, which is used to determine the time point or period when a certain legal event or legal effect exists. For example, the time of birth, the time of death, etc. are time points; The period of limited capacity and the duration of specific rights are all time periods, that is, periods.
As far as the combined effect is concerned, the date and period play a more complex role in the form of constituting legal facts, that is, to cause the occurrence of a certain legal effect. If the period is combined with the fact that the right is not exercised, the limitation of action will be constituted, and the legal consequences of the right of defense will occur. The system of time limit runs through the whole civil law: for example, the date of birth or death of a natural person is decisive for determining the generation and elimination of the capacity for civil rights; If it fails to perform its obligations beyond the time limit for performance of the contract, it shall be liable for delay in performance; The term of validity of the trademark right determines the duration of the right; The term of the suretyship determines the term of the rights and obligations between the creditor and the surety.
The time limit is divided into three types: first, the legal time limit, which is directly stipulated by law, such as the date of full civil capacity, the limitation period of action, etc; The second is to set a time limit, which shall be determined by the people's court or relevant authorities, such as the debt payment period specified in the judgment, the time for the divorced party to visit their children, etc; The third is the agreed time limit, which is determined by the parties' agreement, such as the time limit for debt performance.
Chapter 10 of the Civil Code consists of 5 articles, which mainly stipulates the unit of calculation of the period, the beginning and end of the period, the extension of the end date of the period, and the legal or agreed period. The mind map is as follows:
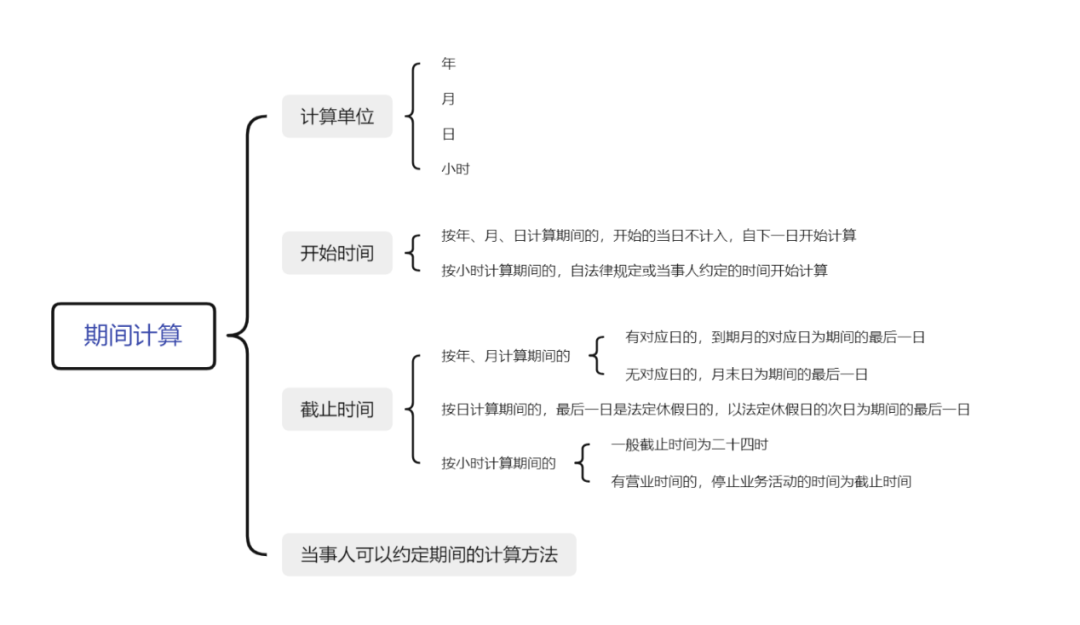
(一) Calculation unit of period: Gregorian calendar year, month, day and hour
Article 200 of the Civil Code originates from paragraph 1 of Article 154 of the General Principles of the Civil Law, which stipulates that "the period referred to in the Civil Code shall be calculated according to the calendar year, month, day and hour." The period calculation generally adopts the combination of calendar calculation method and natural calculation method. Among the four units of time calculation stipulated in this Law, the calendar rules of the Gregorian calendar are used for the year and month. In this way, the time gap between years is not much different, which conforms to both the social reality of our country and the general international rules, and is convenient for production, life and international exchanges. The day and hour are calculated naturally, and the day is 24 hours. As for time units such as week, minute and second, the legal provisions cannot be exhaustive and comprehensive. At the same time, the parties' autonomy and trading habits should be respected in civil activities. Subsequent provisions will also refer to the calculation unit and method that allow the parties to agree on a period.
(二) Period starts
Article 201 of the Civil Code originates from the second paragraph of Article 154 of the General Principles of Civil Law.
1、If the period is calculated on the basis of year, month and day, the starting day shall not be included, and the period shall be calculated from the next day
To facilitate the understanding of the terms, we take an example by deductive method. For example, Party A and Party B signed a contract on January 1, 2021, the implementation date of the Civil Code.
Period calculated by year: Both parties agree to deliver goods within 3 years in the contract, starting from January 2, 2021, and the deadline for delivery is January 1, 2021. The starting point of overdue liquidated damages and limitation of action is January 2, 2024.
Period calculated by month: Both parties agree to deliver goods within 3 months in the contract, starting from January 2, 2021, and the deadline for delivery is April 1, 2021. The starting point of overdue liquidated damages and limitation of action is April 2, 2021.
The calculation period is based on the days: both parties agree in the contract to deliver goods within 90 days, starting from January 2, 2021, and the deadline for delivery is April 1, 2021. The starting point of overdue liquidated damages and limitation of action is April 2, 2021. If the two parties entered into an agreement on January 1, 2024, and the agreed delivery date was 90 days, the deadline for delivery would be March 31, 2021, and the starting point of liquidated damages for delay and limitation of action would be April 1, 2024.
Note: when the calculation unit is year and month, the results of period calculation are not affected by the number of days of each natural month, leap year and average year in a year; The number of days in each natural month in a year is different, and the number of days in February in leap year and normal year is also different. The same period length may produce different calculation results in different months and years. As an attorney, we should pay special attention to the starting point of overdue liquidated damages and limitation of action under different calculation units, which relates to the final amount of liquidated damages and whether there is the possibility of time limitation defense.
2、If the period is calculated in hours, it shall start from the time stipulated by law or agreed by the parties
Compared with the provisions of the General Principles of the Civil Law, this article allows the parties to agree when the period is calculated by the hour. This is to respect the party's autonomy of will, the trading habits of different regions and industries to the maximum extent, facilitate life and promote transactions.
As far as the Civil Procedure Law is concerned, it should be noted that Article 125 of the Judicial Interpretation of the Civil Procedure Law stipulates that "in accordance with the provisions of Paragraph 2 of Article 82 of the Civil Procedure Law, the period counting from time in civil proceedings starts from the second hour; the period counting in days, months and years starts from the next day." This clearly stipulates the standard that the period counting from time starts from the second hour, and the people's court specifies that the relevant period shall be calculated in accordance with this provision, At the same time, it can also be applied by reference when there is no special agreement between the parties in the civil substantive law or no clear provisions in the law.
(三) End of period
1、If the period is calculated by year or month, the date corresponding to the maturity date is the last day of the period; If there is no corresponding day, the month end is the last day of the period
Article 202 of the Civil Code is a new article. The General Principles of the Civil Law does not make a general provision on the expiration date of the period, which leads to different understandings in theory and practice. If the term is calculated on a monthly basis as stipulated in Item 2 of Article 107 of the Negotiable Instruments Law, it shall be calculated on the opposite day of the due month; If there is no corresponding date, the end of the month shall be the due date. On the basis of summing up the opinions of all parties, the General Principles of Civil Law put forward the concept of "corresponding date", which clearly stipulates that if the period is calculated by year and month, the corresponding date of the expiration month is the last day of the period; If there is no corresponding day, the end of the month is the last day of the period, which is of great significance for guiding and standardizing the civil subject's behavior and unifying the judgment scale.
To facilitate understanding, let's also take an example: Party A and Party B signed a contract on February 29, 2020, and the starting date of the performance period is March 1, 2020. If the agreed time limit for performance is half a year or six months, the deadline for performance is August 31, 2020; If the agreed time limit for performance is one year or twelve months, the deadline for performance is February 28, 2021.
2、If the last day of a period is a statutory holiday, the last day of the period shall be the day following the end of the statutory holiday
The content of the first paragraph of Article 203 of the Civil Code originates from the third paragraph of Article 154 of the General Principles of the Civil Law, which is about the extension of the end date of the period. The last day of the period is the statutory holiday, which will have a significant impact on the emergence, change or elimination of civil legal acts. Therefore, the period stipulated by law shall be postponed to the first day after the end of the statutory holiday. If Party A and Party B sign a contract on February 2, 2022, stipulating that the performance period is 8 months, the deadline for the expiration of the performance period is October 2, 2022. Since the last day of the period is a statutory holiday, the performance will expire on October 8, 2022, the day after the end of the holiday. Specific provisions on statutory holidays may refer to the Measures for Holidays on National Annual Festivals and Memorial Days promulgated by the State Council.
3、The deadline for the last day of the period is 24:00; If there is time for business activities, the time for stopping business activities is the deadline
The content of the second paragraph of Article 203 of the Civil Code originates from the fourth paragraph of Article 154 of the General Principles of Civil Law, which is about the end point of the end of the period. There are 24 hours in a day, and 24:00 is the end point of the day. However, banks, stock exchanges, etc. have business hours. When they arrive at the business time, the business will stop operating. At the time contact point, the business end time is more meaningful. It is unnecessary to stipulate that the business will end at 24:00, which is more in line with the actual situation of social life.
(四) The calculation method of the period can be agreed
Article 204 of the Civil Code is a new article, which stipulates: "The calculation method of the period shall be in accordance with the provisions of this Law, unless otherwise provided by law or agreed by the parties." First, if there are different provisions on the calculation method of the period in the separate method, the provisions of the special law shall apply in light of the special principle which is superior to the general principle of law; Second, fully respect the party's autonomy of will. The parties may have specific trading habits or freely agree on the calculation method for the period. For example, the parties may agree to adopt the calculation unit of the lunar calendar year, half month, week, working day, etc. as the calculation period.
There are both differences and connections between this Article and paragraph 2 of Article 201. Article 201 The provision only refers to that, in the case of a period calculated by hours, the parties may agree on the starting point for the beginning of the period; The provisions of this article refer to the calculation method of the period agreed by the parties, which has not only the starting point but also the ending point, and has a wider scope of application. In addition, if the provisions of the Civil Procedure Law on the time limit for filing a case, the time limit for appeal, and the time limit for applying for retrial belong to the statutory period, they should be handled in accordance with the law.
So far, not only the limitation and period clauses have ended, but also the analysis of 204 articles in the General Provisions has been completed. Later, it will be included in the property rights section. For the absolute rights of possession, use, income and disposal, registration has the effect of publicity and credibility. There are many specific provisions on the specific rights of ownership, usufruct and security interest. Next time, we will first analyze the general rules of property rights, what are the basic provisions in this part, what are the principles and rules for the establishment, change, transfer and elimination of property rights, and how to protect property rights. Please refer to the next set of General Rules of Property Rights, "Tao" listens to "Tu" theory<Civil Code>General Rules of Property Rights.

 沪公网安备 31010602001694号
沪公网安备 31010602001694号