DeBund|Legal Acts in the General Provisions of the Civil Code (Part I)
Civil legal act is the abstraction and generalization of a series of behaviors that can produce specific rights and obligations, such as contract behavior, marriage behavior, will behavior, etc. it is an important civil system for civil subjects to realize their intentions in civil activities. The thinking map of civil legal acts in Chapter VI of the civil code is as follows:
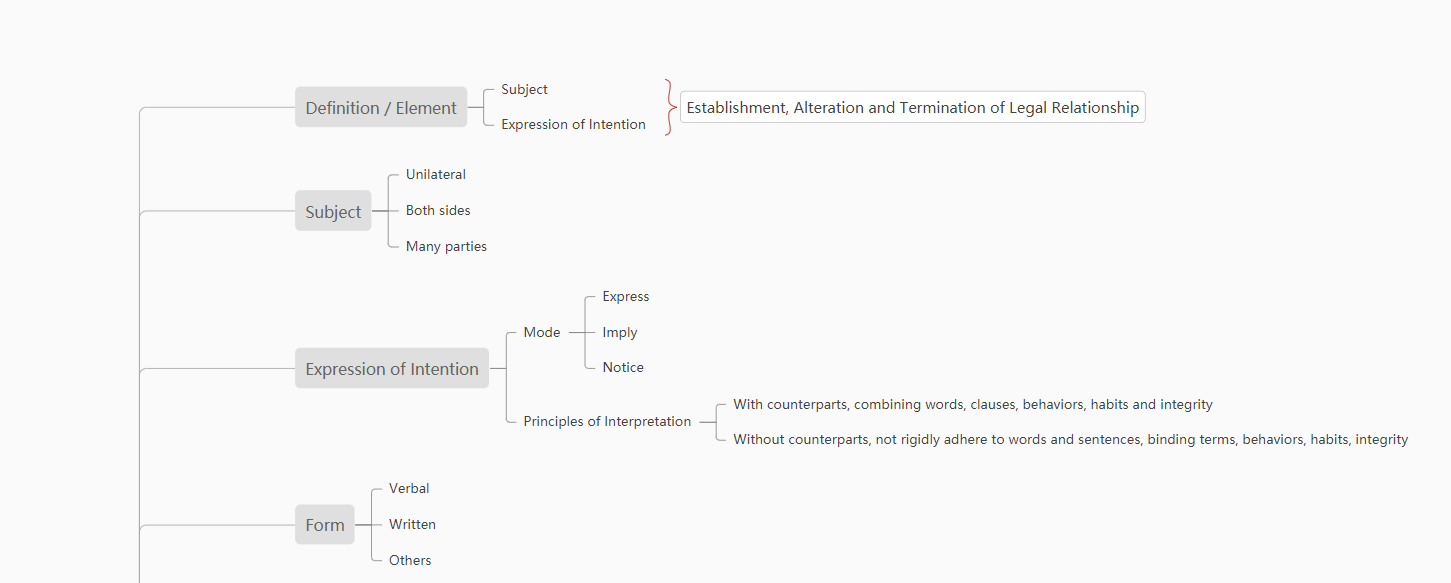

I、 Elements of civil legal act
Civil legal acts are performed by the civil subject through the expression of will, so the two constituent elements are "civil subject" and "expression of will".
i. Civil subject
The civil subject has the capacity for civil rights and civil conduct, and enjoys civil rights and assumes civil obligations. Civil activities are all done by civil subjects. As the sender, transmitter, receiver of the expression of will and the bearer of rights and obligations, civil subjects are the necessary elements of civil legal acts. Different civil legal acts can be distinguished from different perspectives of civil subjects.
1. According to the category of civil subjects, civil legal acts can be divided into natural persons, legal persons and unincorporated organizations.
Article 54 of the original 1986 general principles of the civil law stipulates that "civil legal acts are citizens or legal persons..." this time, the civil code inherits the provisions of Article 133 of the 2017 general principles of the civil law, and uniformly modifies "citizens or legal persons" to "civil subjects". On the one hand, civil subjects are more abstract and generalized. At the moment of the continuous deepening and popularization of civil law theory, using basic concepts to define them can not only accurately describe, It is also convenient and accurate to understand; Second, the concept of "civil subject" is more rigorous and comprehensive. "Citizen" is a concept used under the planned economic system and the concept of public law. Natural persons have been used since the general provisions of the civil law in 2017, and the latest civil subjects are divided into natural persons, legal persons and unincorporated organizations, which are no longer citizens and legal persons stipulated in the general provisions of the civil law in 1986.
2. According to the number and direction of civil subjects, it can be divided into unilateral, bilateral, multilateral civil legal acts and resolution civil legal acts.
Unilateral civil juristic act refers to a civil juristic act that can be established independently only by the expression of one party's will. Specifically, it can be divided into unilateral juristic acts that do not involve the interests of others, such as the abandonment of property and unilateral juristic acts that involve the interests of others, such as making a will and giving property; The civil legal act of both parties is a civil legal act that is established only when the expression of will between the parties is opposite and consistent. The most typical is the contract; Multi party civil juristic act is a civil juristic act that is established when the expression of intention of more than three parties is opposite and consistent. The most typical is to determine the articles of association and sign the partnership agreement.
A resolution civil juristic act is a civil juristic act in which two or more parties express their will in the same direction and intend to achieve a certain legal effect based on the common expression of will. The characteristics are reflected in three aspects: (1) the resolution forms the expression of will in the way of majority decision, pursues the principle that the minority is subordinate to the majority, and does not require the consistency of expression of will; (2) Resolutions must be made in accordance with the rules of procedure and voting procedures agreed by law or jointly agreed; (3) In principle, the resolution is only applicable to the internal agreed matters between the parties. After the formation of the resolution, it will be effective externally through unilateral, bilateral and multilateral legal acts. The effectiveness of civil legal acts of resolutions of profit-making legal persons can be systematically analyzed and studied in combination with Article 85 of the civil code and articles 1 to 5 of judicial interpretation IV of the company law. Limited to the theme and length, it is not explained in detail here. Interested readers can find the above regulations and corresponding applicable cases.
Derivation: with the continuous development of the concept of "civil legal act", changes have also taken place in the legislative norms. The civil legal act stipulated in the general principles of civil law in 1986 has two characteristics: (1) only legal acts can be called civil legal acts, and invalid and revocable acts can be called civil acts; (2) There is no emphasis on the core position of expression of intention in civil legal acts. The civil code inherits the 2017 general provisions of the civil law and transforms the connotation of civil legal acts as "substantive amendments": first, the concept of civil acts is unscientific, because it cannot cover civil acts with undetermined effectiveness; Secondly, considering that the concept of civil legal act is deeply rooted in the hearts of the people, this legal term is still used to give new connotation, that is: (1) all civil acts engaged in by civil subjects, including legal acts, invalid acts, revocable acts and acts with undetermined effectiveness, are collectively referred to as civil legal acts; (2) It emphasizes that the essential feature of civil legal act is "expression of will" and adds six new clauses for this purpose, which is more comprehensive in logic, more self consistent in theory, and closer to the theory of German civil law, the birthplace of the word "legal act".
ii. Expression of intention
Expression of will is the core element of legal act, which is essentially expression of will. A legal act may be a single direction expression of intention, a two-way consistent expression of intention, or a common expression of intention in multiple directions, but it can never be without expression of intention. Freedom of marriage, family autonomy and the spirit of contract are all achieved through the expression of will. It emphasizes that when the parties engage in civil activities according to their own wishes, it also reminds the parties that they should bear the corresponding legal consequences. Whether it is a legal act, invalid act, revocable act, or an act with undetermined effect, it is essentially a legal act implemented based on the expression of will, and the actor should be responsible for his expression of will.
Specifically, "expression of will" refers to an act that indicates externally that it intends to have a certain legal effect in private law. According to the traditional civil law theory, the constituent elements of expression of will can be summarized as the following five kinds, namely, the intention of act, the intention of expression, the intention of purpose, the intention of effect, and the act of expression. In short, it is the behavior that the actor expresses his inner meaning to the outside in a certain way in order to produce a certain civil law effect.
In our country, which has the tradition of "meaning is greater than words", and the language has rich meanings, the word meaning is worth pondering, "who is interesting", "who is interesting", "how many meanings", "what is the meaning" and "there is no meaning at all". In different contexts, scenes and even different moods, meanings have different meanings. The real intention and attitude of the interlocutor need to be analyzed in detail. Therefore, the meaning itself is very "interesting", and the thing itself is not "thing". When international friends first see "give some color to see", they often understand it as whether it is red orange yellow green blue purple. Of course, coincidentally, the West also has slang, such as jump the gun, have the hike.
Therefore, there are often tensions and cracks between the richness and scenariousness of language and characters, the experience and background of the communicators themselves, and the certainty and rigor of legal requirements. As an elder said, "a legal person should strive to write a document with one meaning for a thousand people, not a thousand Hamlets". How to convey and understand meaning expression is worth studying and analyzing.
1. Communication and reception of intention
(1) Expression of intention with and without counterpart
There are many types of expression of will. According to whether it is made to the opposite party, it can be divided into the expression of will with the opposite party and the expression of will without the opposite party. The expression of intention of the opposite party refers to the expression of intention made to a specific object, such as the offer and acceptance to conclude a contract, the expression of intention to cancel, change or terminate the contract; The expression of intention without counterpart means that there is no need to express intention to a specific object or to an unspecified object, such as a reward advertisement or a discarded object. Whether there is a counterpart or not, there is the transmission of intention. In the case of a counterpart, we should pay more attention to the reception of intention.
(2) Conversational expression and non conversational expression
There is the meaning expression of the opposite party, which can be divided into conversational meaning expression and non conversational meaning expression according to different ways of expression. The expression of intention made in the form of dialogue refers to the expression of intention made by the ideograph in a way that enables the opposite party to receive it synchronously, without time difference, such as face-to-face, telephone communication, QQ chat, wechat voice and video, etc. Since it is received synchronously, the effective time of the expression of the intention of the ideograph is the time when the relative person knows its content. The expression of intention made by non dialogue means that the time made by the ideograph is not synchronized with the time received by the opposite party, and there is a time difference between the two, such as letters, faxes, e-mails, etc. Other countries and regions have four kinds of legislation on when the expression of non dialogue will take effect: expressionism, Messenger doctrine, arrival doctrine and understanding doctrine. Because arrival doctrine takes into account the interests of the ideograph and the opposite party, China's civil legislation and most countries or regions have adopted arrival doctrine. The original contract law stipulates that the offer and acceptance of the parties shall take effect when they reach the other party. The civil code continues the practice of the contract law, adopts the doctrine of arrival, and only modifies and improves the specific form carrier of the non dialogue mode.
(3) Traditional letter form and data message form
There is the expression of non dialogue intention of the opposite party, which can be divided into traditional letter form and data message form according to different form carriers. Traditional letters take the arrival of mail as the effective time. Then, when is it deemed to arrive when the meaning is expressed in data messages? The contract law refers to the provisions of the model law on electronic commerce formulated by the United Nations Commission on international trade law. If the recipient designates a specific system to receive data messages, the time when the data messages enter the specific system is deemed to be the time of arrival; If no specific system is specified, the first time that the data message enters any system of the recipient is deemed to be the time of arrival. The second paragraph of Article 37 of the civil code has made certain development on the basis of continuing the provisions of the contract law, which is divided into three levels: first, if the opposite party designates a system to receive data messages, the data messages will take effect when they enter the specific system; Second, if no specific system is designated, the opposite party knows or should know that the data message takes effect when it enters the system; Third, if the parties have otherwise agreed on the effective time of the expression of intention in the form of data messages, such agreement shall prevail.
In terms of trial practice, after a dispute occurs, the ideograph should bear the burden of proof that the expression of intention has taken effect, especially if the opposite party has not designated a specific system, the ideograph should provide evidence to prove that the opposite party knows or should know the time when the data message enters its system. However, it is difficult for the ideograph to prove that the opposite person knows or should know. In order to balance the interests of the ideograph and the opposite party, the United Nations Convention on the use of electronic communications in international contracts stipulates that when a data message arrives in the recipient's system, the recipient should be presumed to know the data message. Once the data message enters the system of the opposite party, it is deemed that the opposite party knows or should know the expression of intention. If the opposite party denies, it must bear the burden of proof that it does not know or should not know.
2. Forms and ways of expression of will
(1) The form of expression of will can be written, oral or other forms.
For the external form of expression of will, there are two modes from legal theory and legislative practice: one mode is that the requirements for form are relatively strict, that the external form affects the security of transactions, in principle, the written form is adopted, and even the notarization form is required, which limits the freedom of the parties to choose; The other mode does not impose mandatory requirements on the form and gives the parties the freedom to choose. Although it is easy to cause disputes and affect the safety of transactions, it is more convenient and efficient, thereby reducing transaction costs. Most countries and regions in the world adopt such legislation. China's civil legislation has adopted a relatively strict legislative model from the early "economic contract law", "technology contract law" and "foreign-related contract law" to the "general principles of civil law", "contract law" and "general provisions of civil law", which can be in written, oral or other forms. If the law stipulates or the parties agree on a special form, the special form shall be adopted.
(2) The ways of expression of will include express, implied and silent.
There are three ways for the actor to express his intention: Express, implied and silent. The first two are expressed through positive behavior, which is expressed orally or in writing, and implied through behavior, which is directly expressed; Silence is a negative omission, but there is no such positive behavior as "showing" in the expression of intention. Silence can be regarded as an expression of will only when it is stipulated by law, agreed by the parties or in line with the trading habits between the parties. From the perspective of system, article 638 of the Civil Code stipulates that when the trial period expires, if the buyer fails to express whether to purchase the subject matter, his silent behavior is presumed to mean purchase. In the settlement of civil and commercial disputes, when the parties claim that their silence or that of the other party should be regarded as an expression of intention, they bear the corresponding burden of proof, citing the corresponding legal provisions, agreements between the parties or trading habits. In the procedural law, there is also the presumption of silence. Article 4 of the provisions on evidence in civil procedure stipulates: "if a party neither acknowledges nor denies the fact that the other party claims to be unfavorable to him, and after being questioned by the adjudicator, it still does not clearly express its affirmation or negation, it is deemed to recognize the fact." Therefore, in order to correct the situation, both men and women are no longer silent.
3. Understanding and interpretation of meaning expression
As mentioned above, all meaning expressions are reflected through certain external forms such as language, words, behavior, etc., and whether these external forms are consistent with the real meaning expression of the ideograph's heart is often different due to the difference of the ideograph's expression ability or expression method, or the meaning expression is unclear and unclear. This leads to the fact that in real life, different people may have different understandings and even disputes about the meaning expression of the ideograph, so it is necessary to explain the meaning expression. Article 142 of the civil code is refined on the basis of the first paragraph of Article 125 of the contract law, and at the same time, it is improved to distinguish between the counterpart and the non counterpart.
The interpretation of the meaning expression of the opposite party needs to consider the real meaning of the ideograph's heart, that is, subjective thoughts; We should also consider the trust interests of the opposite party, that is, the objective situation, and consider the two together. Theoretically, it is also known as the combination of subjective and objective hermeneutics; The biggest difference between the interpretation rules of expression of will without relative person is that, because there is no relative person, the interpretation of this expression of meaning mainly explores the inner true meaning of the ideograph, and less consideration is given to the objective situation, which is called subjective interpretionism in theory.
Therefore, the interpretation of "the expression of the will of the opposite party should be based on the words and sentences used, combined with the relevant terms, the nature and purpose of the behavior, habits and the principle of good faith", that is, based on the textual interpretation, it should adopt the interpretation of system, purpose, habits and the principle of good faith. "The interpretation without the expression of the will of the opposite party cannot be completely confined to the words and sentences used, but should be combined with the relevant provisions, the nature and purpose of the behavior, habits and the principle of good faith". It is equally applicable to the interpretation of text, system, purpose, habits and the principle of good faith to explore the true meaning of the parties.

 沪公网安备 31010602001694号
沪公网安备 31010602001694号